What Is Carbon-Negative Cement and Why Is It the Future of Construction?
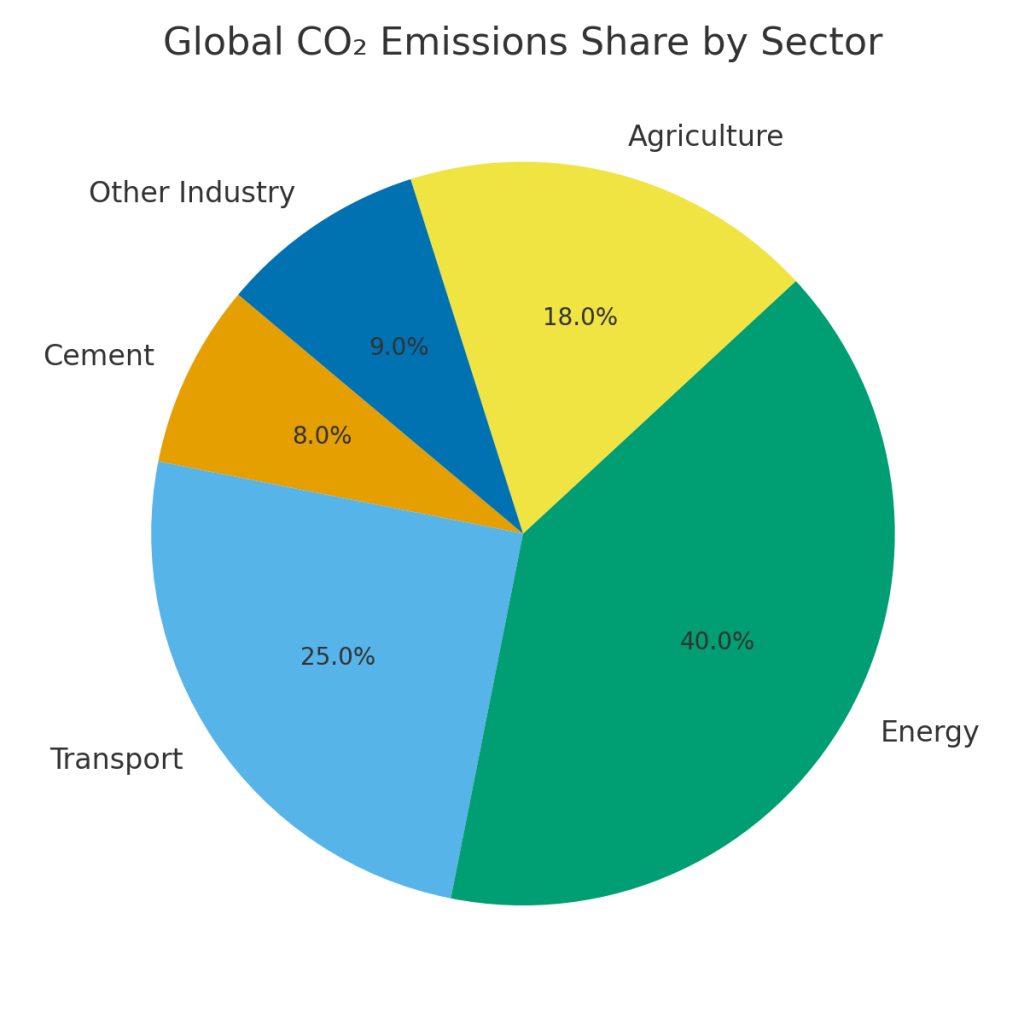
The global construction industry has long been criticized for its carbon footprint, with cement production alone accounting for nearly 8% of global CO₂ emissions. This figure is alarming given the world’s ambitious climate targets. To achieve net-zero building materials and sustainable cities, the industry needs disruptive solutions.
One of the most promising developments is carbon-negative cement — a material designed not only to reduce emissions but to actively sequester CO₂ during its lifecycle. Unlike traditional cement, which is energy- and carbon-intensive, this innovation transforms the very foundation of construction into a climate solution.
How Is Carbon-Negative Cement Different from Traditional Cement?
To understand its importance, let’s compare:
- Traditional Cement (OPC)
- Relies on limestone calcination, releasing large amounts of CO₂.
- Energy-intensive kilns powered by fossil fuels.
- Every ton of cement releases ~0.9 tons of CO₂.
- Carbon-Negative Cement
- Uses alternative feedstocks like magnesium silicates, fly ash, or slag.
- Absorbs CO₂ during curing through carbon mineralization.
- Some processes even integrate direct carbon capture from industrial emissions.
- Result: More CO₂ stored than emitted.
This shift makes carbon-negative cement a cornerstone of sustainable cement technology.
What Innovations Power Sustainable Cement Technology?
Several approaches are transforming how cement is made:
- CO₂-Sequestering Concrete
- Captures and locks CO₂ into stable minerals during curing.
- Reduces emissions while improving material strength.
- Alternative Binders
- Replaces limestone with non-carbonate rocks, industrial waste, or biomass ash.
- Lowers emissions and enhances durability.
- Carbon Capture Integration
- Directly connects cement plants to carbon capture utilization (CCU) systems.
- Converts emissions into valuable building materials.
- Energy Efficiency
- New kilns operate at lower temperatures.
- Integration of renewable energy sources for heating.
These low-carbon cement innovations position the industry for a greener future.
What Is the Market Outlook for Carbon-Negative Cement?
The demand for green construction materials is surging as governments and corporations commit to net-zero targets.
- The global cement and concrete market is worth over $400 billion annually. Even capturing a small share with carbon-negative solutions could represent tens of billions in revenue.
- By 2030, the carbon-negative cement market is projected to surpass $40–50 billion, supported by regulatory shifts and rising investor interest.
- Venture capital and climate funds are increasingly backing low-carbon cement startups.
Regional Highlights
- Europe: Aggressive policies under the European Green Deal support rapid adoption.
- North America: Strong growth driven by U.S. federal infrastructure investments and carbon credit markets.
- Asia-Pacific: Massive construction demand paired with climate commitments creates the largest potential growth market.
This shows that carbon-negative cement is both a climate solution and a business opportunity.
What Do Patents Reveal About Carbon-Negative Cement Innovation?
Patent activity provides a clear picture of technological maturity:
- Rapid Growth: Patent filings related to carbon-negative cement surged after 2010, particularly in carbon capture curing and new binder technologies.
- Technology Readiness: Most innovations are now at TRL 7–9, moving from pilot scale to full commercialization.
- Key Patent Areas:
- CO₂ mineralization methods.
- Integration of carbon capture in cement plants.
- Bio-based and waste-based binders.
- High-strength low-carbon composites.
Patent leaders include LafargeHolcim, Heidelberg Materials, CarbonCure, Solidia, Blue Planet, and emerging green construction startups.
Which Companies Are Leading in Carbon-Negative Cement?
Industry Giants
- Holcim (LafargeHolcim) – Scaling carbon capture and mineralization projects worldwide.
- Heidelberg Materials – Investing in full-scale CCU cement plants in Europe.
- https://www.cemex.com/CEMEX – Active in partnerships with tech companies for net-zero building materials.
Startups Driving Innovation
- CarbonCure Technologies – CO₂ injection during mixing, already deployed in hundreds of plants.
- Solidia Technologies – Cement that cures with CO₂, reducing emissions by up to 70%.
- Blue Planet Systems – Converts captured CO₂ into synthetic limestone.
- Brimstone Energy – Produces cement from silicate rocks, bypassing limestone emissions.
These players represent the backbone of the sustainable cement technology ecosystem.
Which Universities and Labs Are Leading Research?
Research is the foundation of innovation. Leading institutions include:
- MIT Concrete Sustainability Hub – Modeling cement emissions and new binders.
- University of Cambridge – Integrating CCU into cement production.
- Stanford University – Developing CO₂-sequestering concrete technologies.
- TU Delft – Bio-cement research using bacteria for mineralization.
- Imperial College London – Life cycle analysis of low-carbon cement innovations.
Such academic work directly feeds into patents and industrial collaborations.
What Are Examples of Real-World Carbon-Negative Cement Projects?
- CarbonCure in North America: Used in thousands of construction projects, from airports to commercial buildings.
- Solidia paving blocks: Piloted in Europe and the U.S. for sidewalks and infrastructure.
- Blue Planet’s synthetic limestone: Used in concrete mixes for California road projects.
- Holcim’s CCU projects: Building Europe’s first large-scale carbon capture cement facility.
These projects prove that carbon-negative cement is not just theoretical — it’s already being deployed.
What Are the Benefits of Carbon-Negative Cement?
Key benefits include:
- Climate impact: Removes more CO₂ than emitted.
- Durability: Stronger, longer-lasting concrete.
- Compliance: Meets green building certification standards.
- Marketability: Appeals to developers seeking sustainable branding.
- Circular economy: Utilizes industrial waste as raw material.
This makes carbon-negative cement a win-win for the environment and industry.
What Challenges Does Carbon-Negative Cement Face?
Even with progress, several barriers remain:
- Cost – Production is still more expensive than ordinary cement.
- Scalability – Moving from pilot plants to mass adoption is difficult.
- Standards & Codes – Many building codes still favor traditional cement.
- Market Awareness – Builders and contractors often resist unfamiliar materials.
- Raw Materials – Dependence on industrial byproducts may limit availability.
Policies, investment, and IP-driven collaboration will be essential to overcome these hurdles.
What Is the Role of Policy in Driving Low-Carbon Cement Innovations?
Governments worldwide are introducing policies to accelerate adoption:
- Carbon taxes make traditional cement more expensive.
- Green building certifications reward carbon-negative cement adoption.
- Public procurement policies mandate low-carbon materials in infrastructure.
- Funding programs support startups and university spinouts.
These policy levers ensure that CO₂-sequestering concrete becomes mainstream.
What Is the Future of Carbon-Negative Cement?
Looking ahead:
- Short-term (1–5 years): More pilot projects and early commercialization.
- Medium-term (5–10 years): Wider adoption in infrastructure projects, driven by carbon credits.
- Long-term (10+ years): Carbon-negative cement becomes a default building material, essential for net-zero construction.
The future is clear: carbon-negative cement is not optional — it is necessary.
How Can PatentsKart Help Innovators in Carbon-Negative Cement?
For startups, corporations, and universities, navigating the patent landscape is key. PatentsKart provides:
- Patent landscaping – Identify white spaces and innovation clusters.
- FTO (Freedom-to-Operate) – Ensure products don’t infringe existing patents.
- Market intelligence – Benchmark competitors and startups.
- Global IP filing – Protect technologies in key regions.
- Strategic partnerships – Connect with research and industry leaders.
With PatentsKart, innovators in sustainable cement technology can secure their position in this booming market.
Conclusion
Carbon-Negative Cement represents a revolutionary shift in construction. By leveraging CO₂-sequestering concrete, sustainable cement technology, and low-carbon cement innovations, the industry can meet its climate commitments while building a profitable future.
Backed by patents, startups, and global research, carbon-negative cement is set to become the foundation of green construction materials.
PatentsKart ensures that innovators protect and scale these breakthroughs, turning climate challenges into business opportunities.
FAQs
1. What is carbon-negative cement in simple terms?
It is cement that absorbs more CO₂ than it emits, making construction climate-positive.
2. How does carbon-negative cement help reduce emissions?
It uses alternative binders, captures CO₂ during curing, and integrates carbon capture technology.
3. Which companies are leaders in carbon-negative cement?
LafargeHolcim, Heidelberg Materials, CEMEX, and startups like CarbonCure, Solidia, and Blue Planet.
4. What are the benefits of CO₂-sequestering concrete?
It strengthens structures, reduces emissions, and supports net-zero building certifications.
5. How can PatentsKart support green cement innovators?
By offering patent protection, FTO studies, and competitive intelligence to help scale globally.