Plastic waste is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of the 21st century. With millions of tons of mixed plastic generated every year, conventional recycling methods struggle to keep up. Mechanical recycling is limited by contamination and material degradation, while landfilling and incineration worsen ecological footprints. A new frontier is emerging—enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste—offering breakthrough pathways for transforming plastic waste into valuable resources.
By combining biological and thermal processes, enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste brings innovation to the circular economy. Enzymatic degradation breaks polymers down at the molecular level, while pyrolysis converts mixed plastics into usable fuels and chemicals. Together, these technologies have the potential to make plastic recycling more sustainable, scalable, and economically viable.
What Is Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling of Mixed Plastic Waste?
Enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste refers to two complementary processes:
- Enzyme-based recycling: Uses engineered enzymes to depolymerize plastics like PET into monomers for reuse.
- Pyrolysis recycling: Applies heat in the absence of oxygen to break down plastics into oil, gas, and char.
By integrating these methods, mixed plastic streams that were once considered “non-recyclable” can now be recovered and reintroduced into production cycles.
Why Is Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling of Mixed Plastic Waste Important?
This dual approach addresses urgent global challenges:
- Scalability: Can handle large, contaminated, or heterogeneous waste streams.
- Sustainability: Reduces reliance on virgin fossil fuels.
- Economic value: Generates feedstock for chemicals, fuels, and new plastics.
- Circular economy: Extends the lifecycle of materials.
- Climate impact: Cuts greenhouse gas emissions compared to landfilling or incineration.
By advancing plastic recycling technology, this approach aligns with global sustainability goals.
How Does Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling of Mixed Plastic Waste Work?
Enzyme-Based Process
- Enzyme engineering: Specialized proteins are designed to target polymer bonds.
- Depolymerization: Plastics are broken down into monomers.
- Purification: Extracted monomers are cleaned and reused in polymerization.
Pyrolysis Process
- Feedstock preparation: Mixed plastic waste is collected and shredded.
- Thermal decomposition: Heated at 400–600°C without oxygen.
- Product recovery: Outputs include pyrolysis oil, syngas, and solid char.
- Integration: Pyrolysis oil can be refined into fuels or used as chemical feedstock.
The synergy of enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste makes it versatile and effective across different plastic types.
What Are the Benefits of Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling of Mixed Plastic Waste?
Key benefits include:
- Broader recycling capacity: Handles plastics that mechanical methods cannot.
- High material recovery: Produces virgin-like monomers and fuels.
- Economic incentives: Creates new markets for recycled products.
- Environmental protection: Diverts waste from oceans and landfills.
- Industrial scalability: Suitable for large-scale waste management systems.
These benefits ensure that enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste is not just a laboratory concept but a real-world solution.
What Are the Applications of Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling?
Applications span across industries:
- Packaging industry: Recycled PET and PE for bottles and containers.
- Textiles: Monomers from enzymatic recycling reused in polyester fibers.
- Energy sector: Pyrolysis oil refined into alternative fuels.
- Chemical industry: Feedstock for resins, lubricants, and solvents.
- Infrastructure: Pyrolysis char used in asphalt and construction.
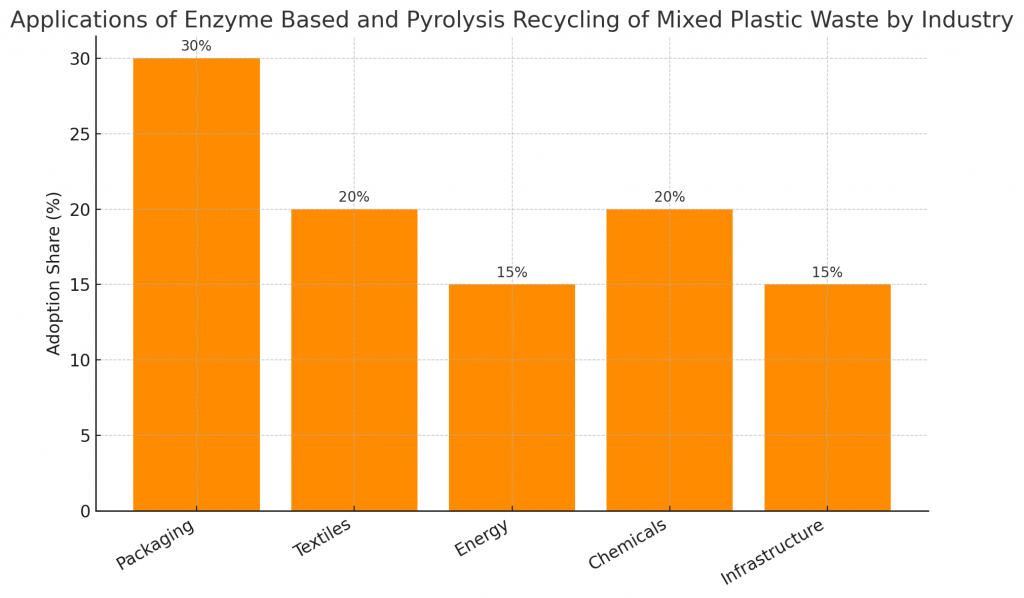
This demonstrates how enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste fuels multiple sectors of the circular economy.
Which Companies Are Leading in This Field?
- Carbios: Pioneer in enzymatic PET recycling.
- Loop Industries: Commercializing enzyme-based depolymerization.
- Brightmark Energy: Specializes in pyrolysis-based plastic-to-fuel plants.
- Plastic Energy: Advanced pyrolysis recycling for circular plastics.
- Neste: Integrating pyrolysis oil into chemical production.
These leaders show how sustainable recycling methods are gaining global traction.
Which Startups Are Innovating?
- Novoloop: Developing enzymatic solutions for upcycling plastics.
- PureCycle Technologies: Focused on high-purity recycled PP.
- BioCellection (now Novoloop): Converting mixed waste into chemicals.
- Agilyx: Operating large-scale pyrolysis plants.
- Gr3n Recycling: Combining microwave-assisted depolymerization with enzymatic methods.
Startups are accelerating the adoption of plastic recycling technology with fresh ideas and agile business models.
What Do Patents and TRL Levels Indicate?
Patent filings show concentration in:
- Enzyme engineering for high-efficiency depolymerization.
- Pyrolysis reactor design for higher yields.
- Integration methods combining bio and thermal recycling.
- Product purification systems for higher-grade outputs.
Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs):
- Enzymatic PET recycling: TRL 7–8, nearing commercialization.
- Pyrolysis plants: TRL 8–9, already operational.
- Mixed waste integration: TRL 5–7, in development.
- Hybrid recycling models: TRL 4–6, early-stage pilots.
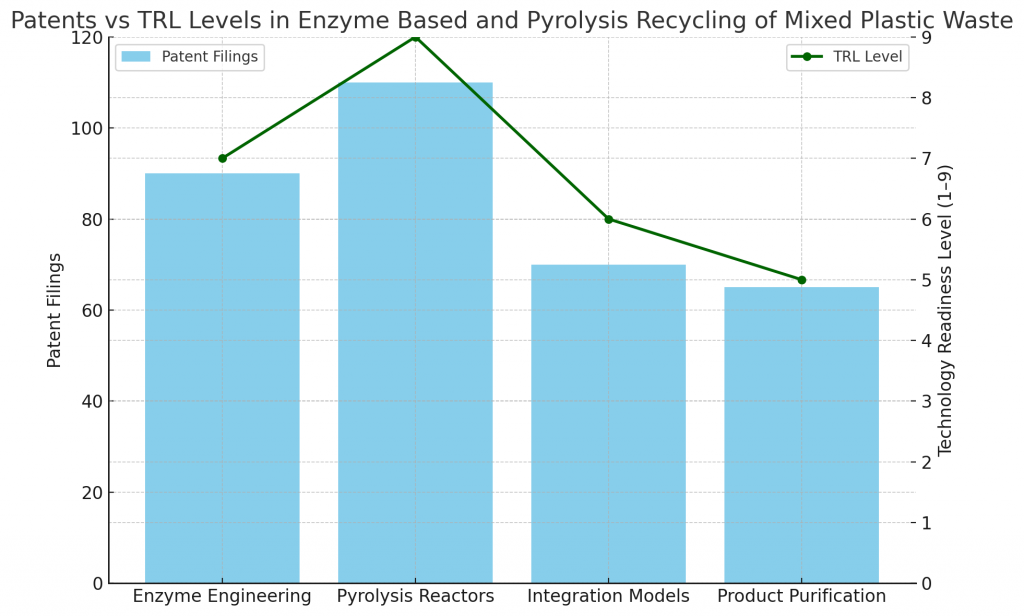
This maturity analysis shows commercial readiness and strong innovation potential.
What Are the Challenges?
Despite promise, barriers remain:
- Cost of enzyme engineering: Requires high R&D investment.
- Energy use in pyrolysis: Needs optimization for sustainability.
- Feedstock contamination: Reduces efficiency and output quality.
- Regulatory hurdles: Approval for recycled materials in food packaging.
- Scale-up challenges: Industrial adoption requires large infrastructure.
Overcoming these challenges will define the pace of adoption for enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste.
What Is the Future Outlook?
The next decade is likely to bring:
- Integration of enzymatic and pyrolysis methods at industrial scale.
- AI-driven waste sorting to improve feedstock quality.
- Policy incentives encouraging circular economy adoption.
- Global expansion of recycling plants in Asia, Europe, and North America.
- Carbon-neutral operations with renewable energy integration.
With these trends, enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste will drive sustainable change in global waste management.
How Can PatentsKart Help?
PatentsKart supports innovators in enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste by offering:
- Patent landscaping to map innovation opportunities.
- Freedom-to-operate studies to reduce litigation risks.
- Competitor analysis for tracking leaders and startups.
- TRL benchmarking to assess technology maturity.
- Licensing support for faster commercialization.
This ensures companies stay competitive while building sustainable recycling solutions.
Conclusion
Plastic waste has long been seen as an unsolvable problem, but enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste is changing that narrative. By combining biological precision with thermal scalability, these technologies offer hope for a world where plastics no longer overwhelm landfills and oceans.
The circular economy depends on solutions like this—ones that balance innovation, sustainability, and economic feasibility. For industries, governments, and innovators, now is the time to invest in the future of recycling.
FAQs About Enzyme Based and Pyrolysis Recycling of Mixed Plastic Waste
Q1. What is enzyme based and pyrolysis recycling of mixed plastic waste?
It is a dual process combining enzymatic depolymerization and thermal pyrolysis to recycle complex plastic waste streams.
Q2. Why is this approach better than traditional recycling?
It can handle contaminated and mixed plastics that mechanical recycling cannot.
Q3. Which companies are leading globally?
Carbios, Brightmark, Plastic Energy, Neste, and Loop Industries.
Q4. What are the main challenges?
High costs, energy usage, contamination issues, and regulatory hurdles.
Q5. How does PatentsKart support innovators in this space?
By providing IP insights, competitor benchmarking, and commercialization strategies.