Fashion is one of the most resource-intensive industries in the world. From animal leather tanning to synthetic fabric dyeing, traditional methods consume water, chemicals, and energy on a massive scale. As consumers and brands shift toward sustainability, a groundbreaking solution has emerged—biofabricated fashion technology.
This innovation combines biology, biotechnology, and design to create lab-grown fabrics, mycelium-based leather, and microbial dyes. By replacing resource-heavy textiles with eco-friendly alternatives, biofabricated fashion technology is transforming the way clothing and accessories are made.
What Is Biofabricated Fashion Technology?
Biofabricated fashion technology refers to the use of biotechnology and lab-based methods to grow or engineer fabrics, dyes, and leathers. Instead of extracting raw materials from animals or petroleum, biofabrication relies on living organisms such as fungi, bacteria, and yeast.
Core elements include:
- Lab-grown leather: Engineered from collagen proteins without harming animals.
- Mycelium textiles: Fungi-derived materials with leather-like strength.
- Microbial dyes: Pigments produced by bacteria instead of chemical dyes.
- Protein-based fibers: Lab-grown silk and spider silk alternatives.
This approach ensures sustainable production while offering new possibilities for fashion design.
Why Is Biofabricated Fashion Technology Important?
The fashion industry faces sustainability challenges:
- Animal welfare concerns: Traditional leather depends on livestock farming.
- Environmental impact: Synthetic fabrics pollute ecosystems with microplastics.
- Resource intensity: Textile dyeing uses 20% of global industrial water pollution.
- Consumer demand: Shoppers seek eco-friendly and cruelty-free alternatives.
- Circular economy: Brands need recyclable and biodegradable fabrics.
By addressing these issues, biofabricated fashion technology is emerging as the cornerstone of sustainable fashion.
How Does Biofabricated Fashion Technology Work?
The process blends biology and design innovation:
- Step 1: Cultivation – Organisms like fungi or yeast are grown in controlled labs.
- Step 2: Engineering – Proteins or fibers are extracted or structured into textile materials.
- Step 3: Processing – Materials are stabilized, dyed with microbial pigments, and shaped into fabrics.
- Step 4: Application – Biofabricated textiles are used in clothing, footwear, and accessories.
This biotech fashion approach ensures low waste, low emissions, and high versatility.
What Are the Benefits of Biofabricated Fashion Technology?
Key benefits include:
- Eco-friendly fabrics: Reduced reliance on water, land, and chemicals.
- Vegan leather alternatives: Cruelty-free yet durable materials.
- Customization: Fabrics engineered for specific textures and performance.
- Biodegradability: Materials break down naturally at end-of-life.
- Market differentiation: Brands gain sustainability credibility.
For both luxury houses and fast fashion retailers, biofabricated fashion technology opens a path toward responsible innovation.
What Are the Applications of Biofabricated Fashion Technology?
Applications extend across fashion and lifestyle industries:
- Apparel: T-shirts, jackets, and dresses made from lab-grown fibers.
- Footwear: Sneakers from mycelium leather and engineered textiles.
- Luxury goods: Designer handbags and accessories using vegan leather.
- Sportswear: Bioengineered fabrics offering strength and elasticity.
- Home interiors: Upholstery and décor items from microbial dyes and fabrics.
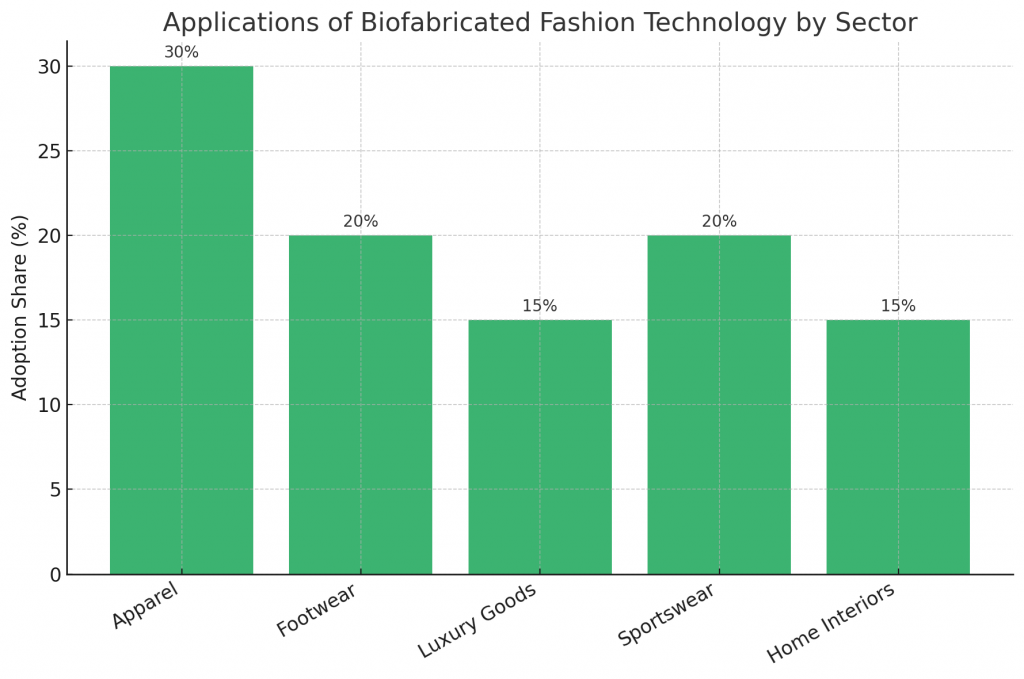
From everyday wear to high-end couture, biofabricated fashion technology has limitless applications.
Which Companies Are Leading in Biofabricated Fashion Technology?
Global leaders include:
- MycoWorks: Mycelium-based Reishi™ leather.
- Bolt Threads: Known for Mylo™ mycelium leather and Microsilk™ fibers.
- Modern Meadow: Collagen-based lab-grown leather.
- Spiber: Lab-grown spider silk fibers.
- Stella McCartney & Adidas: Early adopters of biofabricated textiles.
These companies are proving that biofabricated fashion technology is commercially viable.
Which Startups Are Innovating in This Field?
Startups driving innovation include:
- VitroLabs: Lab-grown leather at pilot scale.
- Colorifix: Microbial dyeing solutions.
- Galy: Lab-grown cotton fibers.
- Biomaterials startups in Asia & Europe: Scaling mycelium and microbial fabrics.
By bridging science and design, startups ensure sustainable fashion reaches the mainstream.
What Do Patents and TRL Levels Indicate?
Patent activity is concentrated in:
- Mycelium leather processing.
- Protein-based silk production.
- Microbial dye fermentation.
- Hybrid textile blending.
Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs):
- Mycelium textiles: TRL 7–8, nearing commercialization.
- Lab-grown leather: TRL 6–7, pilot plants active.
- Microbial dyes: TRL 7–8, early adoption by brands.
- Lab-grown silk: TRL 5–6, still scaling.
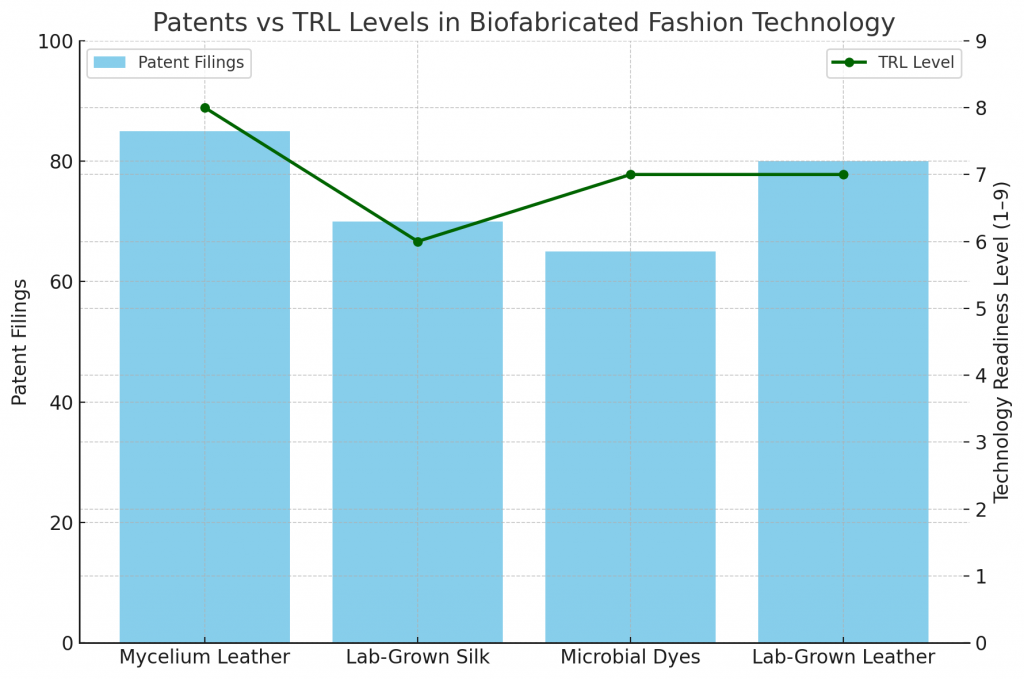
This shows maturity in some areas while signaling potential growth in others.
What Are the Challenges in Adoption?
Challenges remain:
- High costs: Lab-grown fabrics are expensive to scale.
- Infrastructure: Requires bioreactors and specialized facilities.
- Consumer acceptance: Shoppers need education on biotech textiles.
- Standardization: Certification and testing frameworks still evolving.
- Investment risks: Scaling startups require significant capital.
Despite these barriers, momentum behind biofabricated fashion technology continues to grow.
What Is the Future Outlook?
The next decade will bring:
- Cost reduction: Economies of scale in production.
- Mainstream adoption: Expansion into fast fashion and mass retail.
- Digital integration: AI-driven material design.
- Global adoption: Especially in Europe, US, and Asia-Pacific.
- Regulatory frameworks: Clear sustainability certifications.
With these trends, biofabricated fashion technology is set to disrupt the fashion industry permanently.
How Can PatentsKart Help?
PatentsKart provides critical support for innovators in biofabricated fashion technology:
- Patent landscaping to identify white spaces.
- Freedom-to-operate analysis to avoid risks.
- Competitor intelligence to track rivals.
- TRL benchmarking to assess market readiness.
- Licensing and partnerships to accelerate commercialization.
This ensures companies stay ahead in the fast-evolving field of biotech fashion.
Conclusion
The fashion industry can no longer rely on outdated, polluting practices. Biofabricated fashion technology offers a powerful alternative, combining biotechnology with creativity. From mycelium leather to microbial dyes, these innovations redefine sustainability and style.
For brands, adopting this technology is more than a trend—it’s a responsibility. For consumers, it means access to eco-friendly, cruelty-free fashion. And for innovators, it opens doors to a truly circular economy.
FAQs About Biofabricated Fashion Technology
Q1. What is biofabricated fashion technology?
It is the use of biotechnology to grow fabrics, leather, and dyes in labs.
Q2. Why is it important for sustainability?
It reduces environmental impact, eliminates animal use, and supports circular textiles.
Q3. Which companies are leaders?
MycoWorks, Bolt Threads, Modern Meadow, Spiber, and Stella McCartney.
Q4. What are the main challenges?
High costs, scalability, and consumer education.
Q5. How can PatentsKart help innovators?
By providing IP insights, TRL benchmarking, and commercialization strategies.