The global energy transition is accelerating, with governments and industries searching for solutions that balance growth with sustainability. Among the most promising pathways are blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications. These fuels combine the advantages of hydrogen and ammonia with carbon capture technologies, enabling lower-emission alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
By bridging conventional energy and renewables, blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications represent practical steps toward net-zero goals. They are scalable, versatile, and capable of decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors like shipping, power generation, and heavy industry.
What Are Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia for Energy Applications?
Blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications are low-carbon fuels derived from natural gas but paired with carbon capture and storage (CCS).
- Blue hydrogen: Produced through steam methane reforming (SMR) or autothermal reforming (ATR), where CO₂ emissions are captured and stored underground.
- Blue ammonia: Ammonia synthesized from blue hydrogen, serving as both a hydrogen carrier and a direct fuel for power and shipping.
Together, they combine the energy density of fossil fuels with lower emissions, making them ideal for large-scale decarbonization.
Why Are Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia Important for Energy Applications?
The importance stems from urgent global challenges:
- Decarbonization: Provides cleaner fuels for industries that cannot easily electrify.
- Energy security: Diversifies supply and reduces dependence on oil and coal.
- Infrastructure compatibility: Can leverage existing pipelines, ports, and refineries.
- Scalability: Large-scale plants make adoption feasible across nations.
- Global climate goals: Support net-zero targets by reducing CO₂ emissions.
With these benefits, blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications are becoming strategic pillars of the energy transition.
How Do Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia for Energy Applications Work?
The production process integrates natural gas reforming with CCS:
- Step 1: Reforming – Natural gas undergoes SMR or ATR to extract hydrogen.
- Step 2: Carbon capture – CO₂ from reforming is captured and sequestered.
- Step 3: Ammonia synthesis – Captured hydrogen is combined with nitrogen to form ammonia.
- Step 4: Utilization – Blue hydrogen is used in refineries, transport, or power, while blue ammonia serves as fuel or hydrogen carrier.
This closed-loop system ensures significant emissions reduction compared to traditional fuels.
What Are the Benefits of Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia for Energy Applications?
Key benefits include:
- Lower emissions: CCS captures up to 90% of CO₂.
- Versatility: Used in electricity, transport, and fertilizers.
- Hydrogen carrier role: Blue ammonia enables global hydrogen shipping.
- Industrial fit: Powers steel, cement, and chemical industries.
- Scalability: Large plants can supply global markets.
These advantages confirm the role of blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications as enablers of sustainable growth.
What Are the Applications of Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia?
Applications span multiple sectors:
- Power generation: Co-firing in coal plants and direct combustion.
- Shipping: Blue ammonia as marine fuel for zero-carbon shipping.
- Heavy industry: Hydrogen for steelmaking and chemical processes.
- Fertilizers: Ammonia remains critical for agriculture.
- Hydrogen economy: Blue ammonia as a storage and transport vector.
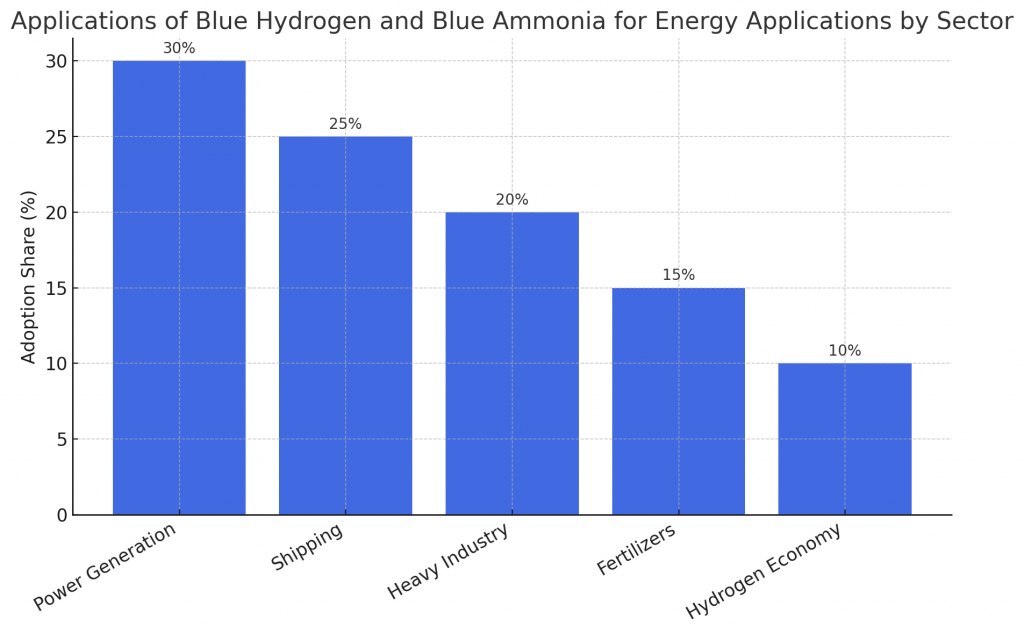
These diverse applications highlight scalability and global relevance.
Which Companies Are Leading in Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia for Energy Applications?
Global corporations investing heavily include:
- Saudi Aramco & SABIC: Pilot shipments of blue ammonia to Japan.
- ExxonMobil: Carbon capture and blue hydrogen hubs.
- Air Products: Large-scale hydrogen and ammonia production projects.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries: Blue ammonia technology development.
- Equinor: Blue hydrogen initiatives in Europe.
These leaders prove how blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications are gaining industrial traction.
Which Startups Are Innovating Rapidly?
Startups and smaller firms are entering the space:
- 8 Rivers Capital: Blue hydrogen and ammonia projects with CCS.
- Horisont Energi: Norwegian startup focusing on blue ammonia exports.
- Monolith Materials: Innovative methane pyrolysis for hydrogen.
- Hydrogenious: Carrier solutions linking blue hydrogen to transport.
- Carbon Clean: Specialized CCS technologies for industrial plants.
These agile players accelerate adoption and reduce technology costs.
What Do Patents and TRL Levels Indicate?
Patent filings show innovation in:
- Carbon capture processes.
- Blue ammonia synthesis techniques.
- Hydrogen carriers and storage.
- Integration with renewable energy.
Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs):
- Blue hydrogen production: TRL 8–9, nearing commercialization.
- Blue ammonia co-firing: TRL 6–7, in pilot projects.
- CCS integration: TRL 7–9, scaling globally.
- Marine fuel use: TRL 5–7, developing rapidly.
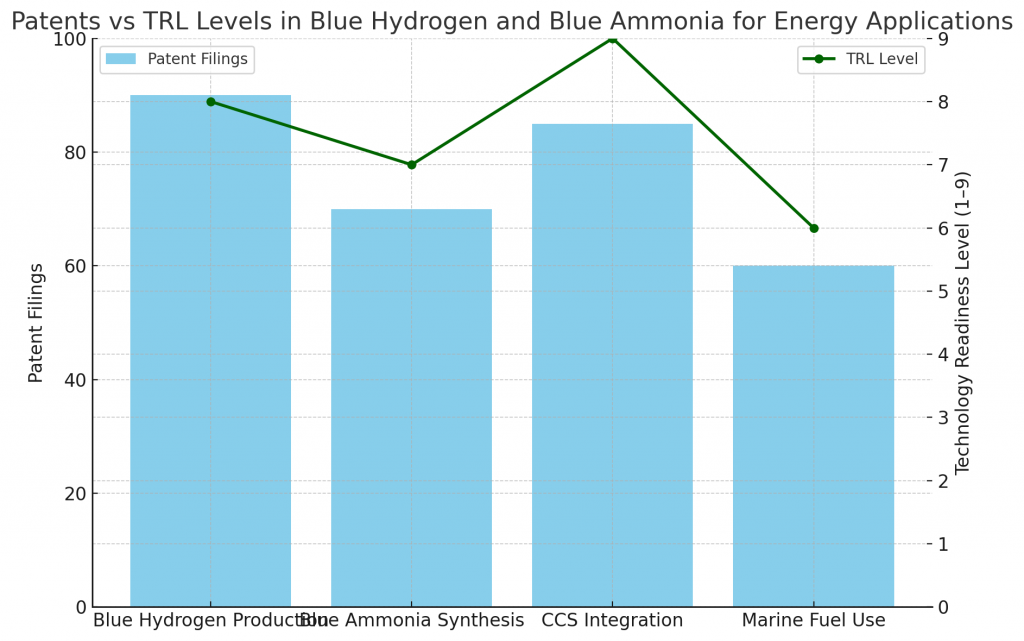
Patent and TRL insights confirm maturity alongside ongoing innovation.
What Are the Challenges in Adoption?
Challenges remain significant:
- High costs: CCS and hydrogen production are capital-intensive.
- Infrastructure gaps: Pipelines, storage, and transport need upgrades.
- Energy penalty: CCS requires additional energy.
- Policy uncertainty: Incentives vary across regions.
- Public perception: Concerns about CO₂ storage safety.
Despite these barriers, momentum for blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications continues to grow.
What Is the Future Outlook?
The future is promising:
- Short term (1–5 years): Pilot projects expand in Asia, Europe, and the U.S.
- Medium term (5–10 years): Widespread adoption in shipping and power.
- Long term (10+ years): Blue fuels complement green hydrogen in global trade.
The outlook confirms blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications as critical pillars of the clean energy transition.
How Can PatentsKart Help?
PatentsKart supports innovators in blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications with:
- Patent landscaping to identify technology gaps.
- Freedom-to-operate analysis to minimize legal risks.
- Competitor benchmarking to track industry leaders.
- TRL benchmarking to map maturity levels.
- Licensing support to speed up commercialization.
This ensures innovators remain ahead in the evolving clean energy landscape.
Conclusion
The world’s clean energy journey requires practical, scalable solutions. Blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications provide exactly that—bridging today’s fossil-fuel-based systems with tomorrow’s renewables.
With strong industry support, advancing technology, and policy backing, these fuels will play a defining role in global decarbonization. The time to invest and innovate in blue fuels is now.
FAQs About Blue Hydrogen and Blue Ammonia for Energy Applications
Q1. What are blue hydrogen and blue ammonia for energy applications?
They are low-carbon fuels made with carbon capture, used for power, shipping, and industry.
Q2. Why are they important?
They enable decarbonization of hard-to-electrify sectors while leveraging existing infrastructure.
Q3. Which companies are leaders?
Aramco, ExxonMobil, Air Products, Mitsubishi Heavy, and Equinor.
Q4. What are the challenges?
High costs, infrastructure gaps, and policy uncertainty.
Q5. How can PatentsKart help innovators?
By offering IP insights, TRL analysis, and commercialization strategies.