Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips are rapidly emerging as a foundational technology for next-generation computing, communication, and sensing systems. As data volumes explode and artificial intelligence workloads strain conventional electronic architectures, this light-based semiconductor technology offers a powerful alternative by using light instead of electrons to transmit and process information.
This blog provides a broad technology landscape of Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips, covering how they work, why they matter, market growth, technology maturity, leading players, applications, and future directions.
What are Integrated Photonic and Optoelectronic Systems?
Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips are semiconductor devices that generate, manipulate, transmit, or detect light on an integrated chip. Unlike traditional electronic chips that rely solely on electrical signals, these chips use photons to move data with minimal resistance and heat loss.
Photonic chips focus on guiding and processing light through waveguides and photonic circuits, while optoelectronic chips combine optical components with electronic control circuitry. Together, these systems enable ultra-high bandwidth, low latency, and energy-efficient data processing.
Why This Technology Matters Today
Modern computing systems are reaching the physical limits of electrical interconnects. Power consumption, heat dissipation, and signal integrity have become major bottlenecks in advanced semiconductor nodes.
These chips address these challenges by:
- Supporting massive data transfer with minimal energy loss
- Reducing latency in data centers and AI accelerators
- Enabling scalable architectures beyond conventional copper interconnects
- Improving performance per watt for high-speed computing
As AI models grow larger and networks move toward 5G and 6G, these chips are becoming strategically critical.
How These Systems Work
These systems integrate multiple optical functions onto a single substrate. Key building blocks include:
- Light sources: Lasers that generate coherent light
- Modulators: Encode electrical data onto optical signals
- Waveguides: Route light across the chip
- Photodetectors: Convert optical signals back into electrical form
- Electronic control circuits: Manage signal processing and logic
By combining these elements, Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips enable seamless interaction between optical and electronic domains.
Core Technologies Powering Integrated Photonic Platforms
Several technologies underpin the development of integrated photonic platforms:
- Silicon photonics: Uses CMOS-compatible silicon to fabricate photonic circuits
- III–V compound semiconductors: Enable efficient light emission and detection
- Hybrid integration: Combines different material platforms on a single chip
- Advanced packaging: Includes co-packaged optics and chiplet integration
- Precision lithography: Ensures low-loss optical pathways
These innovations are driving rapid improvements in performance, yield, and scalability.
Technology Readiness and Commercial Maturity
The maturity of integrated photonic platforms varies across applications. Silicon photonics and optical transceivers have reached high levels of commercial readiness, while optical computing and fully photonic processors remain in earlier stages.
Overall, the technology is transitioning from niche deployments to mainstream adoption, particularly in data centers and high-performance computing environments.
Market Size and Growth Outlook
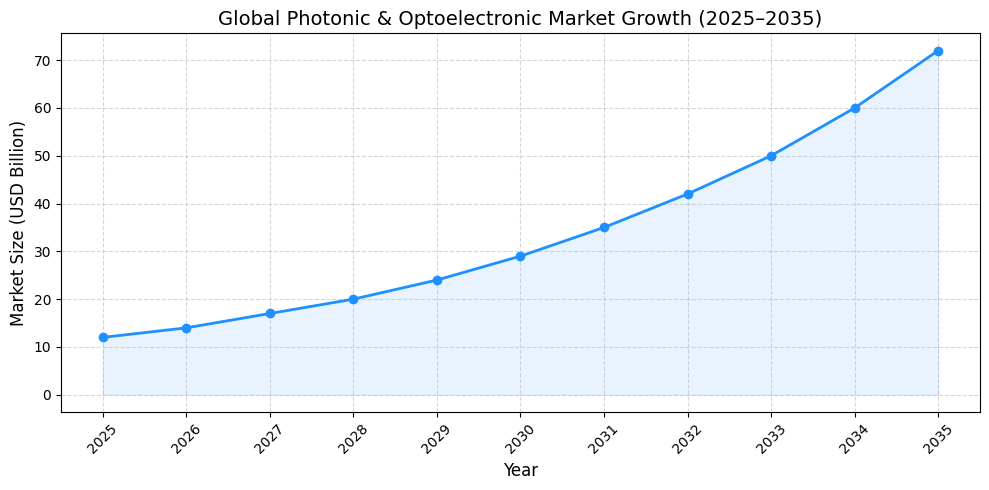
The global market for optoelectronic semiconductor solutions is experiencing strong growth, driven by cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and next-generation communication networks.
Demand from hyperscale data centers, AI accelerators, and telecom infrastructure is expected to fuel sustained expansion over the next decade, positioning Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips as a core component of future semiconductor ecosystems.
Leading Companies Driving Innovation
Major technology companies are investing heavily in advanced photonic hardware to overcome scaling limits in electronic systems.
Established industry leaders include:
Innovative startups and scale-ups include:
- Ayar Labs
- Lightmatter
- Lightelligence
- Celestial AI
- Rockley Photonics
- POET Technologies
- Ranovus
- DustPhotonics
- Luminous
- Ephos
- Xscape Photonics
Together, these companies are accelerating commercialization across data centers, AI hardware, and advanced networking platforms.
Universities and Research Ecosystem
Academic institutions and research organizations play a crucial role in advancing this research domain. Leading contributors include:
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
- Stanford University
- University of California, Berkeley
- IMEC
- CEA-LETI
- University of Southampton
- Eindhoven University of Technology
- Tsinghua University
- Nanyang Technological University
Their research spans materials, device physics, photonic integration, and next-generation optical computing architectures.
High-Value Applications
These technologies enable a wide range of high-impact applications:
- Data centers and hyperscale cloud computing
- AI accelerators and high-performance computing
- Optical interconnects for chip-to-chip communication
- 5G and future 6G networks
- Automotive LiDAR and sensing systems
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
- Quantum computing interfaces
- Defense and aerospace systems
These applications highlight the broad, cross-industry relevance of the technology.
Challenges and Adoption Barriers
Despite strong momentum, several challenges remain. Manufacturing complexity, packaging costs, thermal management, and standardization gaps continue to slow mass adoption.
Addressing these issues will require close collaboration between chip designers, foundries, equipment suppliers, and system integrators.
Future Roadmap
In the short term, adoption will focus on optical transceivers and co-packaged optics in data centers. Medium-term developments include optical I/O for AI accelerators and tighter integration with electronic processors.
Over the long term, these platforms may enable optical computing paradigms and play a key role in quantum and neuromorphic systems.
How PatentsKart Can Help
PatentsKart supports innovation in photonics and optoelectronics through patent search, patent landscape analysis, freedom-to-operate (FTO) studies, patent drafting and filing, and patent portfolio management. These services help organizations protect core technologies, manage IP risks, and build strong, defensible positions in highly competitive semiconductor markets.
Conclusion
Photonic and Optoelectronic Chips are reshaping the future of computing, communication, and sensing. By leveraging the unique advantages of light-based processing, they offer a scalable path beyond the limits of traditional electronics.
For researchers, startups, and enterprises alike, this is a critical moment to invest in innovation, secure intellectual property, and prepare for the next era of semiconductor technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are photonic and optoelectronic chips?
Photonic and optoelectronic chips are semiconductor devices that use light to transmit, process, or detect information. They offer higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved energy efficiency compared to purely electronic chips.
Why are photonic and optoelectronic chips important for AI and data centers?
They reduce data movement bottlenecks, lower power consumption, and support high-speed communication, making them ideal for AI accelerators and large-scale data centers.
Are photonic and optoelectronic chips commercially available today?
Yes, many photonic and optoelectronic chips are already deployed in optical transceivers and data center interconnects, with broader adoption underway.
How do photonic chips differ from electronic chips?
Electronic chips rely on electrical signals, while photonic chips use light, enabling faster data transfer with less heat and energy loss.
What is the future of photonic and optoelectronic chips?
The future includes deeper integration with electronic processors, optical computing, and applications in quantum technologies and advanced AI systems.