What is Soil Carbon Sequestration and Why is it Important?
Soil carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide in the soil. This happens naturally through plant roots, microorganisms, and organic matter. In recent years, it has become a major focus for climate change mitigation, sustainable farming, and carbon credit markets.
Why? Because soils are the largest terrestrial carbon sink. By improving agricultural practices and monitoring soil health, we can increase the amount of carbon stored underground. This directly reduces greenhouse gases in the atmosphere while also improving soil fertility, water retention, and crop productivity.
But the real challenge lies in measuring, monitoring, and verifying (MRV) soil carbon sequestration at scale. That’s where advanced technologies, patents, research, and new companies come into play.
How Big is the Market for Soil Carbon Sequestration?
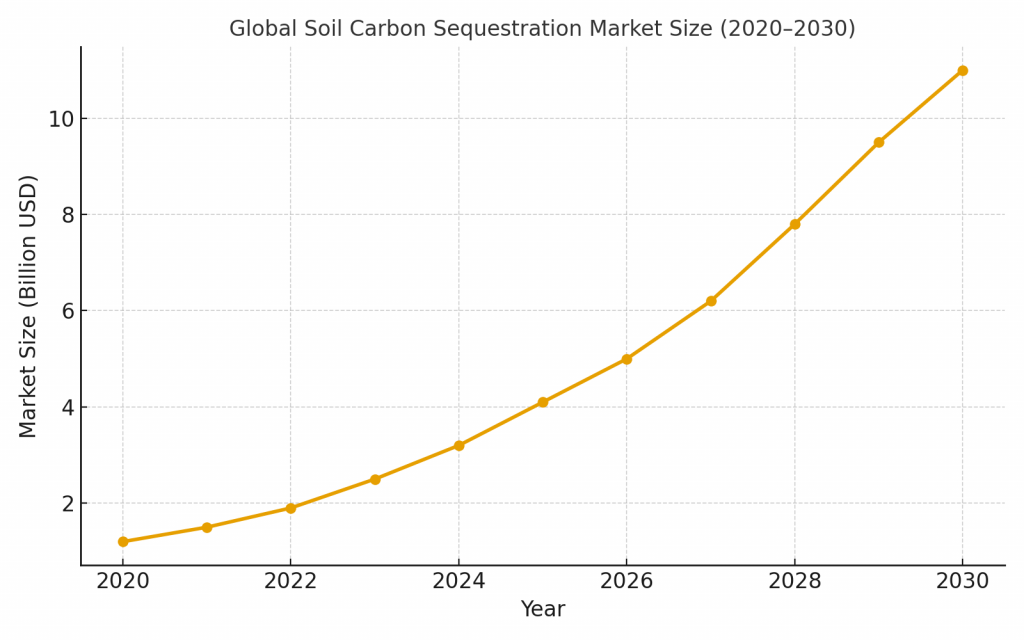
The soil carbon sequestration market is growing rapidly, driven by demand for carbon credits and sustainability programs. According to industry reports, billions of dollars are flowing into carbon farming and regenerative agriculture.
Key growth drivers include:
- Voluntary carbon markets where corporations buy carbon offsets.
- Government policies and incentives supporting sustainable farming.
- Consumer demand for climate-friendly food and supply chains.
- Private investors funding soil carbon startups and MRV platforms.
By 2030, the market for SCS credits is expected to be a multi-billion-dollar industry. Farmers, agritech companies, and carbon marketplaces are racing to build solutions that ensure soil carbon measurement is accurate, verifiable, and affordable.
What is the Role of Patents in Soil Carbon Sequestration?
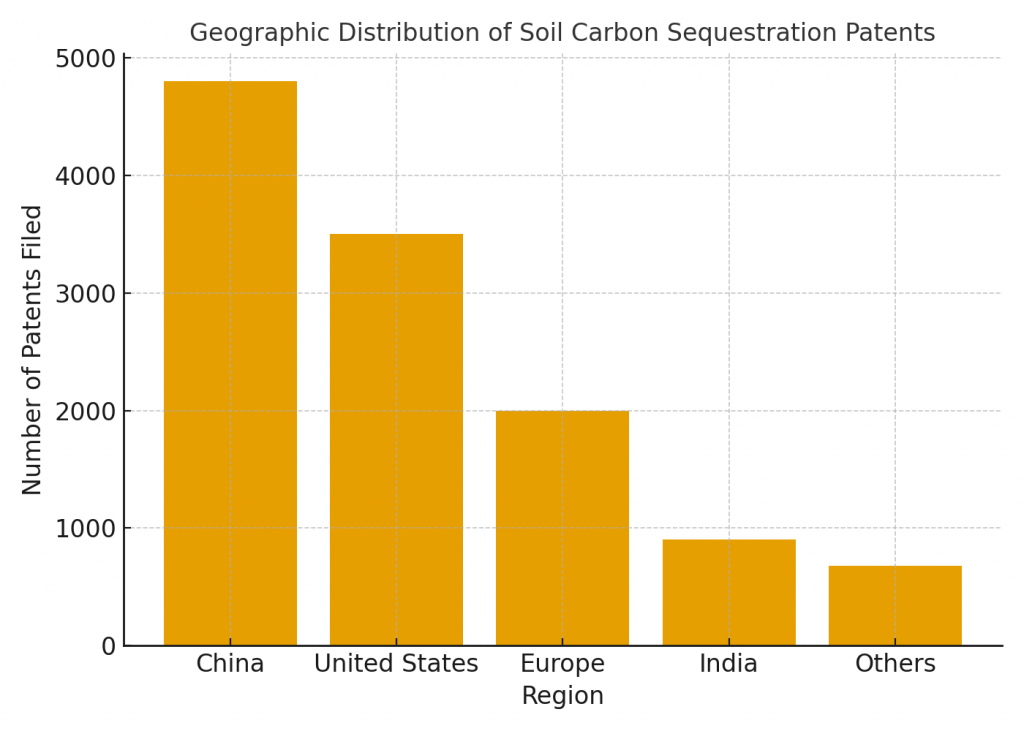
Patents play a critical role in shaping this industry. From new methods of remote sensing to AI-powered soil analysis, intellectual property defines who leads the market.
Highlights from recent patent trends:
- Over 11,000 patents have been filed globally in soil carbon measurement and sequestration technologies.
- China and the United States dominate filings, especially in machine learning, spectroscopy, and data fusion.
- Major patent areas include soil organic carbon (SOC) monitoring, carbon MRV, carbon storage modeling, and IoT-enabled sensors.
Patents not only protect innovation but also signal technology readiness levels (TRL). Many soil carbon sequestration methods are already at TRL 9 (commercial stage), meaning solutions are ready for large-scale deployment.
Which Companies are Leading in Soil Carbon Sequestration?
Several companies are investing heavily in soil carbon sequestration technologies. They fall into different categories:
SOC Measurement and Monitoring
- EarthOptics – Soil mapping using advanced sensors.
- Yard Stick – Proximal soil carbon measurement tools.
- SmartCloud Farming – 3D soil carbon mapping.
Carbon Programs and Credits
- Indigo Ag – Carbon credit programs for farmers.
- Boomitra – AI + satellite monitoring for carbon credits.
- Pachama & Sylvera – Verification and rating platforms for carbon credits.
Agritech and Data Platforms
- John Deere – Integrating soil monitoring into farm machinery.
- Trimble & CropX – Data-driven precision farming solutions.
- Trace Genomics – Soil microbiome analytics.
These companies represent a mix of startups and established agribusiness giants, all converging on soil carbon sequestration as a new growth frontier.
Which Startups are Innovating in Soil Carbon Sequestration?
Startups are driving innovation in carbon MRV (Measurement, Reporting, Verification) by combining AI, remote sensing, and blockchain.
Notable examples:
- Regrow Ag (formerly FluroSat) – Climate-smart farming and carbon credit MRV.
- Deep Planet – Satellite-based soil health monitoring.
- Albo & Cur8 – Marketplaces for verified carbon credits.
- Charm Industrial – Bio-oil carbon storage solutions.
These startups are agile and attract significant venture capital. They are solving the accuracy challenge in carbon monitoring, which is key for scaling the carbon credit market.
How are Universities Contributing to Soil Carbon Sequestration Research?
Universities and research institutes are central to advancing soil carbon knowledge. They contribute through field trials, AI models, and spectroscopy research.
Leading institutions include:
- Federation University (Australia) – Soil carbon modeling.
- University of Huddersfield & Curtin University – AI-driven SOC estimation.
- Zhejiang University & LUT University – Remote sensing and carbon flux studies.
- University of Wisconsin–Madison & Iowa State – Long-term soil research plots.
These universities work closely with governments, NGOs, and industry consortia to standardize methods and push science into practice.
What Standards and Protocols Guide Soil Carbon Sequestration?
Standards are essential for credibility in soil carbon MRV. Without them, carbon credits risk being unreliable.
Key standards include:
- ISO/CD TS 21251 – Biochemical stability of soil organic carbon.
- ISO 23400:2021 – Carbon and nitrogen stock measurement at field scale.
- ISO/DIS 27928 – Guidelines for carbon capture and storage.
- WRI CCS Guidelines & The Climate Registry – Widely used for carbon reporting.
Consortia like CIRCASA, Soil Carbon IRC, and ESMC (Ecosystem Services Market Consortium) ensure consistency across regions. These frameworks are vital for scaling trust in soil carbon sequestration markets.
What Technologies Power Soil Carbon Sequestration Monitoring?
Technology is at the heart of soil carbon measurement. Some of the most promising include:
- Remote sensing & hyperspectral imaging for large-scale monitoring.
- AI & machine learning models to estimate SOC stocks and predict sequestration.
- IoT soil sensors for real-time in-field measurements.
- Spectroscopy (NIR, MIR) for laboratory and portable testing.
- Data fusion methods combining satellite, drone, and ground samples.
These innovations make soil carbon monitoring cheaper, faster, and more scalable.
What are the Challenges in Soil Carbon Sequestration?
Despite progress, soil carbon sequestration faces barriers:
- Measurement accuracy – Soil variability makes monitoring difficult.
- Verification costs – High expenses limit farmer adoption.
- Policy gaps – Lack of global uniformity in carbon credit standards.
- Farmer incentives – Adoption depends on whether carbon credits are profitable.
- Permanence – Ensuring stored carbon stays underground for decades.
Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between scientists, governments, companies, and farmers.
What is the Future of Soil Carbon Sequestration?
The future looks promising with:
- Hyperspectral satellites providing global soil carbon maps.
- Blockchain and AI making MRV more transparent.
- Carbon marketplaces connecting farmers with buyers.
- Public-private partnerships funding large-scale adoption.
- Integration with supply chains as companies demand low-carbon products.
In 5–10 years, soil carbon sequestration could become a mainstream agricultural practice, unlocking both climate and economic benefits.
How Can PatentsKart Help in Soil Carbon Sequestration Innovation?
At PatentsKart, we specialize in guiding innovators, startups, and companies in the soil carbon sequestration space.
Here’s how we can help:
- Patent landscaping – Identify opportunities in soil carbon MRV technologies.
- Freedom-to-operate analysis – Ensure your solutions don’t infringe existing patents.
- IP strategy – Protect your innovations and strengthen your market position.
- Technology scouting – Spot emerging trends and competitors.
- Patent filing and prosecution – Secure your intellectual property globally.
Whether you are a startup building soil carbon monitoring tools or an enterprise launching a carbon credit program, PatentsKart ensures your innovations are protected and strategically positioned.
Conclusion
Soil carbon sequestration is more than a climate solution—it’s a revolution in how we think about farming, sustainability, and the economy. With billions at stake in carbon credits, rapid advancements in AI and remote sensing, and growing involvement from companies, startups, and universities, the opportunity is massive.
However, success depends on standards, patents, and reliable verification methods. This is where IP strategy becomes essential. With the right protection and market intelligence, innovators can lead in shaping the soil carbon economy.
FAQs
1. What is soil carbon sequestration in agriculture?
Soil carbon sequestration in agriculture refers to practices like cover cropping, reduced tillage, and regenerative farming that increase carbon stored in the soil.
2. How is soil carbon sequestration measured?
It is measured using soil sampling, spectroscopy, remote sensing, and AI models that estimate soil organic carbon levels.
3. What are the benefits of soil carbon sequestration?
Benefits include climate change mitigation, improved soil fertility, better water retention, biodiversity support, and new income streams from carbon credits.
4. How can PatentsKart support soil carbon sequestration innovators?
PatentsKart helps innovators with patent analysis, filing, IP strategy, and competitive intelligence to protect and commercialize soil carbon technologies.
5. Which companies are leading soil carbon sequestration technologies?
Companies like Indigo Ag, EarthOptics, Yard Stick, Boomitra, and John Deere are leading in measurement, monitoring, and carbon credit programs.