The digital economy depends on vast data centers powering everything from streaming services to artificial intelligence. Yet with rising computing demand, heat management has become one of the biggest challenges. Traditional air-based cooling struggles to keep pace with dense server racks, leading to inefficiency, downtime risks, and skyrocketing energy bills. A new solution is gaining traction—chilled door for server rack in data center cooling systems.
By integrating liquid-cooled doors directly onto racks, this technology provides localized, high-capacity thermal management. Unlike legacy HVAC systems, a chilled door for server rack in data center targets the heat at its source, ensuring optimal performance while reducing overall energy consumption. This combination of precision and efficiency is reshaping the way IT infrastructure is designed for the future.
What Is a Chilled Door for Server Rack in Data Center Cooling?
A chilled door for server rack in data center cooling system is a rear-door heat exchanger that attaches directly to the back of a server rack. It uses chilled liquid—often water or a special coolant—circulating through the door to absorb and remove heat generated by servers.
Key components include:
- Heat exchanger door: Mounted on the back of the rack.
- Coolant circulation system: Pipes deliver and return chilled liquid.
- Airflow integration: Fans push warm air across the chilled coils.
- Monitoring systems: Sensors ensure efficiency and safety.
This direct-to-rack approach enables scalable, modular cooling that keeps pace with modern IT loads.
Why Is a Chilled Door for Server Rack in Data Center Important?
Modern servers generate extraordinary heat due to high processing densities. Relying solely on raised-floor air conditioning is no longer sufficient. A chilled door for server rack in data center provides:
- Localized cooling: Targets hot spots directly at the rack.
- Energy efficiency: Reduces reliance on massive HVAC systems.
- Scalability: Works with incremental rack deployments.
- Sustainability: Cuts power usage effectiveness (PUE) ratios.
- Reliability: Prevents overheating-related downtime.
In an era where IT infrastructure underpins global business, these advantages are critical.
How Does a Chilled Door for Server Rack in Data Center Work?
The process is straightforward but effective:
- Step 1: Servers generate hot exhaust air.
- Step 2: Air passes through the chilled door’s heat exchanger.
- Step 3: Liquid coolant absorbs heat.
- Step 4: Warm liquid returns to the chiller for re-cooling.
- Step 5: Cooled air re-enters the room, maintaining stable temperatures.
By leveraging liquid cooling systems, a chilled door for server rack in data center delivers far greater efficiency than traditional methods.
What Are the Benefits of a Chilled Door for Server Rack in Data Center Cooling?
Benefits extend across operations, cost, and sustainability:
- Higher density support: Enables racks exceeding 30–40 kW.
- Lower operational costs: Reduces energy demand for cooling.
- Green IT advantage: Supports energy-efficient servers and corporate sustainability goals.
- Flexibility: Compatible with new builds or retrofits.
- Reduced noise: Less reliance on large air handlers.
By adopting thermal management solutions like chilled doors, operators create data centers ready for AI-driven workloads and beyond.
What Are the Applications of Chilled Door Systems?
Applications cut across the global data economy:
- Hyperscale data centers: Meeting the needs of cloud giants.
- Enterprise IT: Supporting high-performance workloads.
- Colocation providers: Offering reliable environments for clients.
- Edge computing: Cooling compact, high-density server deployments.
- AI and HPC clusters: Handling extreme workloads in research and industry.
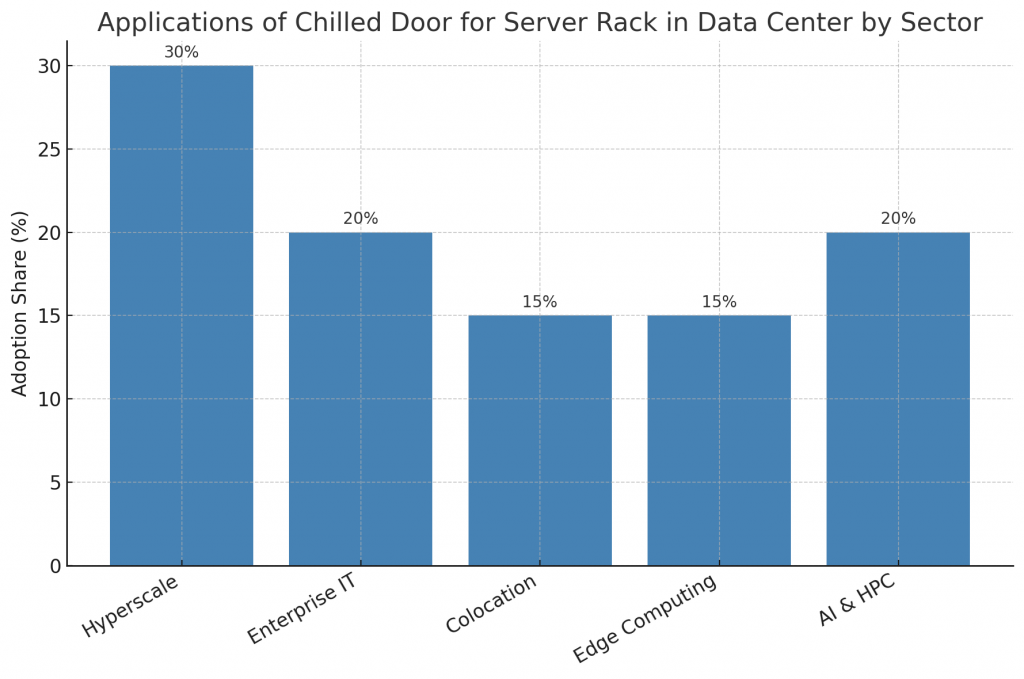
Each application demonstrates how a chilled door for server rack in data center becomes central to future-ready IT infrastructure.
Which Companies Are Leading in This Field?
Several companies are innovating:
- IBM: Early adopter of rear-door heat exchangers for HPC.
- Vertiv: Produces scalable chilled door solutions for enterprise and hyperscale.
- Schneider Electric: Focused on sustainable cooling systems.
- CoolIT Systems: Specialized in liquid cooling technologies.
- Stulz: Provides precision cooling for mission-critical environments.
These firms show how data center cooling technology is evolving around chilled door innovation.
Which Startups Are Innovating?
- Submer: Specializing in immersion and liquid cooling.
- ZutaCore: Waterless two-phase cooling systems.
- Iceotope: Precision immersion paired with chilled solutions.
- GRC (Green Revolution Cooling): Modular cooling platforms for data centers.
- LiquidStack: High-performance cooling for extreme IT loads.
While not all are focused exclusively on chilled doors, their contributions in thermal management solutions complement this approach.
What Do Patents and TRL Levels Indicate?
Patent activity is concentrated in:
- Heat exchanger design for compact efficiency.
- Coolant distribution systems for racks.
- Sensor-driven optimization of liquid cooling.
- Hybrid cooling frameworks combining air and liquid methods.
Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs):
- Rear-door exchangers: TRL 9, already in deployment.
- Hybrid systems: TRL 7–8, piloted in advanced centers.
- Next-gen fluids: TRL 5–7, still in R&D.
- AI-optimized systems: TRL 6–7, emerging in smart data centers.
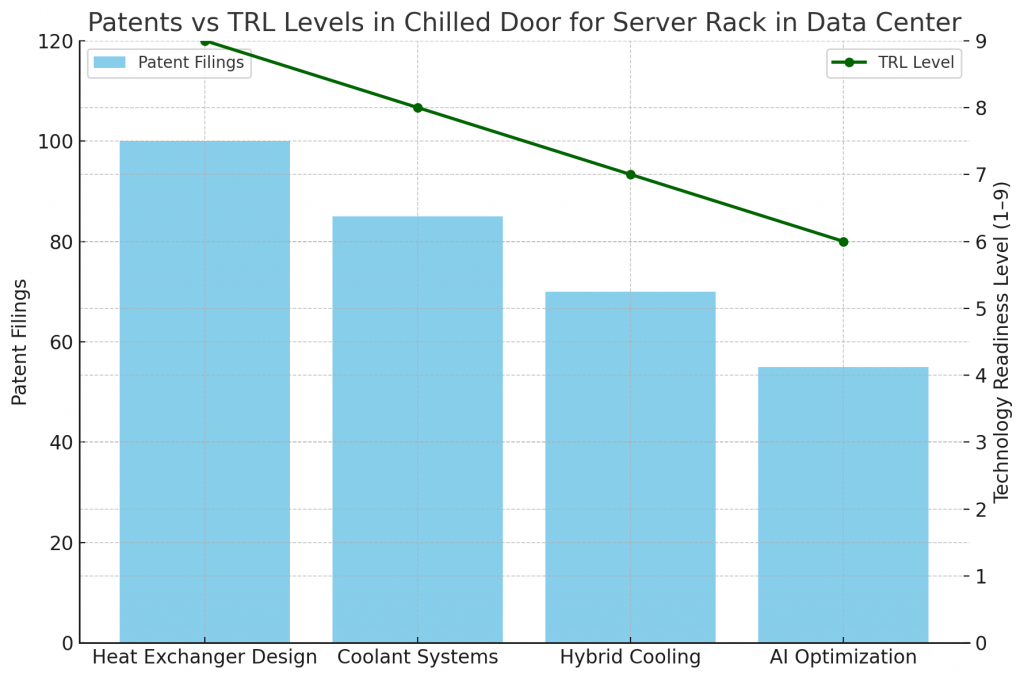
Together, these trends confirm maturity while signaling future innovation opportunities.
What Are the Key Challenges?
Adoption is promising but not without challenges:
- Upfront costs: Higher than legacy air systems.
- Infrastructure integration: Requires piping and coolant loops.
- Maintenance skills: Technicians must handle liquid systems.
- Redundancy: Cooling failure could impact racks directly.
- Market education: Operators may hesitate to move beyond air cooling.
Despite these hurdles, momentum around chilled door for server rack in data center is growing steadily.
What Is the Future Outlook?
Looking forward, expect to see:
- AI integration: Predictive monitoring for proactive cooling.
- Sustainable refrigerants: Eco-friendly coolants replacing traditional fluids.
- Global adoption: Expansion across Asia-Pacific and emerging markets.
- Standardization: Industry-wide frameworks for liquid cooling adoption.
- Net-zero alignment: Helping operators meet emissions targets.
These trends make chilled door for server rack in data center systems indispensable for high-performance IT landscapes.
How Can PatentsKart Help?
PatentsKart provides tailored support for innovators:
- Patent landscapes to identify opportunities and white spaces.
- Freedom-to-operate analysis to mitigate IP risks.
- Competitor tracking to understand the landscape.
- TRL benchmarking to align research with market readiness.
- Licensing and partnerships to accelerate deployment.
For companies developing chilled door for server rack in data center solutions, PatentsKart ensures innovation is protected and commercialized effectively.
Conclusion
The future of data centers depends on cooling that is both efficient and sustainable. Chilled door for server rack in data center systems deliver on this promise by offering localized, scalable, and eco-friendly solutions.
By reducing energy demand, enabling higher densities, and supporting global digital growth, this innovation is redefining thermal management. For enterprises, cloud providers, and innovators, the time to adopt is now.
FAQs About Chilled Door for Server Rack in Data Center
Q1. What is a chilled door for server rack in data center cooling?
It is a rear-door heat exchanger using chilled liquid to cool servers directly at the rack.
Q2. Why is this better than traditional cooling?
It is more energy-efficient, scalable, and effective for high-density racks.
Q3. Which companies lead this technology?
IBM, Vertiv, Schneider Electric, CoolIT, and Stulz are key players.
Q4. What challenges exist?
Costs, infrastructure requirements, and specialized maintenance are barriers.
Q5. How does PatentsKart help innovators?
By offering IP insights, TRL mapping, and strategic support for commercialization.